The Primary Causes And Treatment Plans Of Achilles Tendinitis
Overview
 Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles tendon, the band of tissue that connects calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to your heel bone. Achilles tendinitis most commonly occurs in runners who have suddenly increased the intensity or duration of their runs. It's also common in middle-aged people who play sports, such as tennis or basketball, only on the weekends. Most cases of Achilles tendinitis can be treated with relatively simple, at-home care under your doctor's supervision. Self-care strategies are usually necessary to prevent recurring episodes. More-serious cases of Achilles tendinitis can lead to tendon tears (ruptures) that may require surgical repair.
Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles tendon, the band of tissue that connects calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to your heel bone. Achilles tendinitis most commonly occurs in runners who have suddenly increased the intensity or duration of their runs. It's also common in middle-aged people who play sports, such as tennis or basketball, only on the weekends. Most cases of Achilles tendinitis can be treated with relatively simple, at-home care under your doctor's supervision. Self-care strategies are usually necessary to prevent recurring episodes. More-serious cases of Achilles tendinitis can lead to tendon tears (ruptures) that may require surgical repair.
Causes
There are a number of causes and risk factors associated with Achilles Tendinitis. One of the most common causes is simply a lack of conditioning. If the tendon, and muscles that connect to the tendon, have not been trained or conditioned, this can lead to a weakness that may result in an Achilles injury. Overtraining is also associated with Achilles Tendinitis. Doing too much, too soon places excessive strain on the Achilles tendon and doesn't allow the tendon enough time to recovery properly. Over time small tears and general degeneration result in a weakening of the tendon, which leads to inflammation and pain. Other causes of Achilles injury include a lack of warming up and stretching. Wearing inadequate footwear, running or training on uneven ground, and simply standing on, or in something you're not meant to. Biomechanical problems such as high arched feet or flat feet can also lead to Achilles injuries.
Symptoms
The pain associated with Achilles tendonitis can come on gradually or be caused by some type of leg or foot trauma. The pain can be a shooting, burning, or a dull ache. You can experience the pain at either the insertion point on the back of the heel or upwards on the Achilles tendon within a few inches. Swelling is also common along the area with the pain. The onset of discomfort at the insertion can cause a bump to occur called a Haglund's deformities or Pump bump. This can be inflammation in the bursa sac that surrounds the insertion of the Achilles tendon, scar tissue from continuous tares of the tendon, or even some calcium buildup. In this situation the wearing of closed back shoes could irritate the bump. In the event of a rupture, which is rare, the foot will not be able to go through the final stage of push off causing instability. Finally, you may experience discomfort, even cramping in the calf muscle.
Diagnosis
Confirming Achilles tendonitis may involve imaging tests. X-rays provide images of the bones of the foot and leg. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is useful for detecting ruptures and degeneration of tissue. Ultrasound shows tendon movement, related damage, and inflammation.
Nonsurgical Treatment
There are a variety of treatments for Achilles tendonitis. These range from rest and aspirin to steroid injections and surgery. Your doctor might suggest, reducing your physical activity, stretching and strengthening the calf muscles, switching to a different, less strenuous sport, icing the area after exercise or when in pain, raising your foot to decrease swelling, wearing a brace or compressive elastic bandage to prevent heel movement, undergoing physical therapy, taking anti-inflammatory medication (e.g., aspirin or ibuprofen) for a limited time, getting steroid injections, Sometimes more conservative treatments are not effective. In these cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the Achilles tendon. If the condition intensifies and is left untreated, there?s a greater risk of an Achilles rupture. This can cause sharp pain in the heel area.

Surgical Treatment
Your doctor may recommend surgery if, after around six months, other treatments haven?t worked and your symptoms are having an impact on your day-to-day life. Surgery involves removing damaged areas of your tendon and repairing them.
Prevention
By properly training the body, an athlete can build the strength of their tendons and muscles. Following a workout and dieting plan, the body will be able to build muscle and strengthen most effectively. Additionally, doing the following can prevent tendinitis. Wearing appropriate shoes will give your foot the support it needs for proper movements of the foot and ankle. Improper movements will put additional stress on your body. Stretching before an athletic activity, Stretching primes the body for a taxing activity. Additionally, this will get your blood flowing and reduce the risk of pulling a muscle. Ask your doctor about orthotics, Custom orthotics can help get your foot into proper alignment. If the foot does not execute proper mechanics, the body will adjust which will cause pain and increase the chances of injury.
 Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles tendon, the band of tissue that connects calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to your heel bone. Achilles tendinitis most commonly occurs in runners who have suddenly increased the intensity or duration of their runs. It's also common in middle-aged people who play sports, such as tennis or basketball, only on the weekends. Most cases of Achilles tendinitis can be treated with relatively simple, at-home care under your doctor's supervision. Self-care strategies are usually necessary to prevent recurring episodes. More-serious cases of Achilles tendinitis can lead to tendon tears (ruptures) that may require surgical repair.
Achilles tendinitis is an overuse injury of the Achilles tendon, the band of tissue that connects calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to your heel bone. Achilles tendinitis most commonly occurs in runners who have suddenly increased the intensity or duration of their runs. It's also common in middle-aged people who play sports, such as tennis or basketball, only on the weekends. Most cases of Achilles tendinitis can be treated with relatively simple, at-home care under your doctor's supervision. Self-care strategies are usually necessary to prevent recurring episodes. More-serious cases of Achilles tendinitis can lead to tendon tears (ruptures) that may require surgical repair.
Causes
There are a number of causes and risk factors associated with Achilles Tendinitis. One of the most common causes is simply a lack of conditioning. If the tendon, and muscles that connect to the tendon, have not been trained or conditioned, this can lead to a weakness that may result in an Achilles injury. Overtraining is also associated with Achilles Tendinitis. Doing too much, too soon places excessive strain on the Achilles tendon and doesn't allow the tendon enough time to recovery properly. Over time small tears and general degeneration result in a weakening of the tendon, which leads to inflammation and pain. Other causes of Achilles injury include a lack of warming up and stretching. Wearing inadequate footwear, running or training on uneven ground, and simply standing on, or in something you're not meant to. Biomechanical problems such as high arched feet or flat feet can also lead to Achilles injuries.
Symptoms
The pain associated with Achilles tendonitis can come on gradually or be caused by some type of leg or foot trauma. The pain can be a shooting, burning, or a dull ache. You can experience the pain at either the insertion point on the back of the heel or upwards on the Achilles tendon within a few inches. Swelling is also common along the area with the pain. The onset of discomfort at the insertion can cause a bump to occur called a Haglund's deformities or Pump bump. This can be inflammation in the bursa sac that surrounds the insertion of the Achilles tendon, scar tissue from continuous tares of the tendon, or even some calcium buildup. In this situation the wearing of closed back shoes could irritate the bump. In the event of a rupture, which is rare, the foot will not be able to go through the final stage of push off causing instability. Finally, you may experience discomfort, even cramping in the calf muscle.
Diagnosis
Confirming Achilles tendonitis may involve imaging tests. X-rays provide images of the bones of the foot and leg. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is useful for detecting ruptures and degeneration of tissue. Ultrasound shows tendon movement, related damage, and inflammation.
Nonsurgical Treatment
There are a variety of treatments for Achilles tendonitis. These range from rest and aspirin to steroid injections and surgery. Your doctor might suggest, reducing your physical activity, stretching and strengthening the calf muscles, switching to a different, less strenuous sport, icing the area after exercise or when in pain, raising your foot to decrease swelling, wearing a brace or compressive elastic bandage to prevent heel movement, undergoing physical therapy, taking anti-inflammatory medication (e.g., aspirin or ibuprofen) for a limited time, getting steroid injections, Sometimes more conservative treatments are not effective. In these cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the Achilles tendon. If the condition intensifies and is left untreated, there?s a greater risk of an Achilles rupture. This can cause sharp pain in the heel area.

Surgical Treatment
Your doctor may recommend surgery if, after around six months, other treatments haven?t worked and your symptoms are having an impact on your day-to-day life. Surgery involves removing damaged areas of your tendon and repairing them.
Prevention
By properly training the body, an athlete can build the strength of their tendons and muscles. Following a workout and dieting plan, the body will be able to build muscle and strengthen most effectively. Additionally, doing the following can prevent tendinitis. Wearing appropriate shoes will give your foot the support it needs for proper movements of the foot and ankle. Improper movements will put additional stress on your body. Stretching before an athletic activity, Stretching primes the body for a taxing activity. Additionally, this will get your blood flowing and reduce the risk of pulling a muscle. Ask your doctor about orthotics, Custom orthotics can help get your foot into proper alignment. If the foot does not execute proper mechanics, the body will adjust which will cause pain and increase the chances of injury.
What Is Pain Under The Heel And Simple Tips To Alleviate It

Overview
Plantar fasciitis is that pain in the bottom of your foot usually in the heel. That pain hurts especially with the first few steps in the morning as you get out of bed. This strange name comes from: "Plantar" means something that belongs to the foot, "fascia" means a band or ligament or a connective tissue, and "itis" means inflammation. You can see in the picture the plantar fascia band as it runs along the foot. This band connects your heel bone to the toes.
Causes
There are a number of plantar fasciitis causes. The plantar fascia ligament is like a rubber band and loosens and contracts with movement. It also absorbs significant weight and pressure. Because of this function, plantar fasciitis can easily occur from a number of reasons. Among the most common is an overload of physical activity or exercise. Athletes are particularly prone to plantar fasciitis and commonly suffer from it. Excessive running, jumping, or other activities can easily place repetitive or excessive stress on the tissue and lead to tears and inflammation, resulting in moderate to severe pain. Athletes who change or increase the difficulty of their exercise routines are also prone to overdoing it and causing damage. Another common cause of plantar fasciitis is arthritis. Certain types of arthritis can cause inflammation to develop in tendons, resulting in plantar fasciitis. This cause is particularly common among elderly patients. Diabetes is also a factor that can contribute to further heel pain and damage, particularly among the elderly. Among the most popular factors that contribute to plantar fasciitis is wearing incorrect shoes. In many cases, shoes either do not fit properly, or provide inadequate support or cushioning. While walking or exercising in improper shoes, weight distribution becomes impaired, and significantly stress can be added to the plantar fascia ligament.
Symptoms
Pain tends to start gradually, often just in the heel, but it can sometimes be felt along the whole of the plantar fascia. The symptoms are initially worse in the morning and mostly after, rather than during, activity. As the condition becomes worse, the symptoms become more persistent.
Diagnosis
Plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed by a health care provider after consideration of a person’s presenting history, risk factors, and clinical examination. Tenderness to palpation along the inner aspect of the heel bone on the sole of the foot may be elicited during the physical examination. The foot may have limited dorsiflexion due to tightness of the calf muscles or the Achilles tendon. Dorsiflexion of the foot may elicit the pain due to stretching of the plantar fascia with this motion. Diagnostic imaging studies are not usually needed to diagnose plantar fasciitis. However, in certain cases a physician may decide imaging studies (such as X-rays, diagnostic ultrasound or MRI) are warranted to rule out other serious causes of foot pain. Bilateral heel pain or heel pain in the context of a systemic illness may indicate a need for a more in-depth diagnostic investigation. Lateral view x-rays of the ankle are the recommended first-line imaging modality to assess for other causes of heel pain such as stress fractures or bone spur development. Plantar fascia aponeurosis thickening at the heel greater than 5 millimeters as demonstrated by ultrasound is consistent with a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. An incidental finding associated with this condition is a heel spur, a small bony calcification on the calcaneus (heel bone), which can be found in up to 50% of those with plantar fasciitis. In such cases, it is the underlying plantar fasciitis that produces the heel pain, and not the spur itself. The condition is responsible for the creation of the spur though the clinical significance of heel spurs in plantar fasciitis remains unclear.
Non Surgical Treatment
Plantar fasciitis can be a difficult problem to treat, with no panacea available. Fortunately, most patients with this condition eventually have satisfactory outcomes with nonsurgical treatment. Therefore, management of patient expectations minimizes frustration for both the patient and the provider.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is rarely used in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. However it may be recommended when conservative treatment has been tried for several months but does not bring adequate relief of symptoms. Surgery usually involves the partial release of the plantar fascia from the heel bone. In approximately 75% of cases symptoms are fully resolved within six months. In a small percentage of cases, symptoms may take up to 12 months to fully resolve.
Prevention
Factors that help prevent plantar fasciitis and reduce the risk of recurrence include. Exercises to strengthen the muscles of the lower leg and ankle. Warming up before commencing physical activity. Maintaining a healthy body weight. Avoiding high heeled footwear. Using orthotic devices such as arch supports and heel raises in footwear, particularly for people with very high arches or flat feet. Daily stretches of plantar fascia and Achilles tendon.
What Triggers Heel Discomfort And Approaches To Prevent It
Overview
If your first few steps out of bed in the morning cause severe pain in the heel of your foot, you may have plantar fasciitis, an overuse injury that affects the sole of the foot. A diagnosis of plantar fasciitis means you have inflamed the tough, fibrous band of tissue (fascia) connecting your heel bone to the base of your toes.
Causes
Patients with tight calf muscles will suffer with excessive pulling of the muscle group on the back of the heel. This in turn creates pulling of other structures that are attached to the heel, including the Plantar Fascia. When the pulling continues for long enough, then inflammation will develop and lead to Plantar Fasciitis. This causes Heel Pain. It is extremely common for patients who increase their level of activity to develop Plantar Fasciitis. Boot camp, running, zumba, recreational walking or other quick movement sports such as tennis or touch football are typical causes of Heel Pain. The sharp increase in exercise is too much for the foot to cope with and the stress on the Plantar Fascia causes inflammation. The Heel Pain that is caused by this inflammation is known as Plantar Fasciitis.
Symptoms
When plantar fasciitis occurs, the pain is typically sharp and usually unilateral (70% of cases).Heel pain worsens by bearing weight on the heel after long periods of rest. Individuals with plantar fasciitis often report their symptoms are most intense during their first steps after getting out of bed or after prolonged periods of sitting. Improvement of symptoms is usually seen with continued walking. Numbness, tingling, swelling, or radiating pain are rare but reported symptoms. If the plantar fascia continues to be overused in the setting of plantar fasciitis, the plantar fascia can rupture. Typical signs and symptoms of plantar fascia rupture include a clicking or snapping sound, significant local swelling, and acute pain in the sole of the foot.
Diagnosis
Most cases of plantar fasciitis are diagnosed by a health care provider who listens carefully to your description of symptoms. During an examination of your feet, your health care provider will have to press on the bottom of your feet, the area most likely to be painful in plantar fasciitis. Because the pain of plantar fasciitis has unique characteristics, pain upon rising, improvement after walking for several minutes, pain produced by pressure applied in a specific location on your foot but not with pressure in other areas, your health care provider will probably feel comfortable making the diagnosis based on your symptoms and a physical examination. Your health care provider may suggest that you have an X-ray of your foot to verify that there is no stress fracture causing your pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
Over-the-counter Orthotics. A soft, over-the-counter orthotic (Prefabricated orthotic) with an accommodating arch support has proven to be quite helpful in the management of plantar fascia symptoms. Studies demonstrate that it is NOT necessary to obtain a custom orthotic for the treatment of this problem. Comfort Shoes. Shoes with a stiff sole, rocker-bottom contour, and a comfortable leather upper combined with an over-the-counter orthotic or a padded heel can be very helpful in the treatment of plantar fasciitis. Anti-Inflammatory Medication (NSAIDs): A short course of over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications may be helpful in managing plantar fasciitis symptoms providing the patient does not have any contra-indications such as a history of stomach ulcers. Activity Modification Any activity that has recently been started, such as a new running routine or a new exercise at the gym that may have increased loading through the heel area, should be stopped on a temporary basis until the symptoms have resolved. At that point, these activities can be gradually started again. Also, any activity changes (ex. sitting more) that will limit the amount of time a patient is on their feet each day may be helpful. A night splint, which keeps the ankle in a neutral position (right angle) while the patient sleeps, can be very helpful in alleviating the significant morning symptoms. A night splint may be prescribed by your physician. Alternatively, it can be ordered online or even obtained in some medical supply stores. This splint is worn nightly for 1-3 weeks until the cycle of pain is broken. Furthermore, this splinting can be reinstituted for a short period of time is symptoms recur.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is usually not needed for plantar fasciitis. About 95 out of 100 people who have plantar fasciitis are able to relieve heel pain without surgery. Your doctor may consider surgery if non-surgical treatment has not helped and heel pain is restricting your daily activities. Some doctors feel that you should try non-surgical treatment for at least 6 months before you consider surgery. The main types of surgery for plantar fasciitis are Plantar fascia release. This procedure involves cutting part of the plantar fascia ligament . This releases the tension on the ligament and relieves inflammation . Other procedures, such as removing a heel spur or stretching or loosening specific foot nerves. These surgeries are usually done in combination with plantar fascia release when there is lasting heel pain and another heel problem. Experts in the past thought that heel spurs caused plantar fasciitis. Now experts generally believe that heel spurs are the result, not the cause, of plantar fasciitis. Many people with large heel spurs never have heel pain or plantar fasciitis. So surgery to remove heel spurs is rarely done.
Prevention
Every time your foot strikes the ground, the plantar fascia is stretched. You can reduce the strain and stress on the plantar fascia by following these simple instructions: Avoid running on hard or uneven ground, lose any excess weight, and wear shoes and orthotics that support your arch to prevent over-stretching of the plantar fascia.
What Causes Heel Pain

Overview
The plantar fascia (a connective tissue structure) stretches from the toes and ball of the foot, through the arch, and connects to the heel bone in three places: outside, center and inside. Normally it helps the foot spring as it rolls forward. It also provides support for the arch of the foot. The plantar fascia helps keep the foot on track, cutting down on oscillation. When the foot over-pronates (rolls to the inside) the plantar fascia tries to stabilize it and prevent excessive roll. In time, the inside and sometimes center connections are overstressed and pull away from their attachments. The first sign is usually heel pain as you rise in the morning. When you walk around, the pain may subside, only to return the next morning. Inflammation and increased soreness are the results of long-term neglect and continued abuse. A heel bone spur may develop after a long period of injury when there is no support for the heel. The plantar fascia attaches to the heel bone with small fibers. When these become irritated they become inflamed with blood containing white blood cells. Within the white blood cells are osteoblasts which calcify to form bone spurs and calcium deposits. The body is trying to reduce stress on that area by building a bone in the direction of stress. Unfortunately, these foreign substances cause pain and further irritation in the surrounding soft tissue.
Causes
You're more likely to develop the condition if you're female, overweight or have a job that requires a lot of walking or standing on hard surfaces. You're also at risk if you walk or run for exercise, especially if you have tight calf muscles that limit how far you can flex your ankles. People with very flat feet or very high arches also are more prone to plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis generally occurs in one foot. Bilateral plantar fasciitis is unusual and tends to be the result of a systemic arthritic condition that is exceptionally rare among athletes. Males suffer from a somewhat greater incidence of plantar fasciitis than females, perhaps as a result of greater weight coupled with greater speed and ground impact, as well as less flexibility in the foot. Typically, the sufferer of plantar fasciitis experiences pain upon rising after sleep, particularly the first step out of bed. Such pain is tightly localized at the bony landmark on the anterior medial tubercle of the calcaneus. In some cases, pain may prevent the athlete from walking in a normal heel-toe gait, causing an irregular walk as means of compensation. Less common areas of pain include the forefoot, Achilles tendon, or subtalar joint. After a brief period of walking, the pain usually subsides, but returns again either with vigorous activity or prolonged standing or walking. On the field, an altered gait or abnormal stride pattern, along with pain during running or jumping activities are tell-tale signs of plantar fasciitis and should be given prompt attention. Further indications of the injury include poor dorsiflexion (lifting the forefoot off the ground) due to a shortened gastroc complex, (muscles of the calf). Crouching in a full squat position with the sole of the foot flat on the ground can be used as a test, as pain will preclude it for the athlete suffering from plantar fasciitis, causing an elevation of the heel due to tension in the gastroc complex.
Diagnosis
X-rays are a commonly used diagnostic imaging technique to rule out the possibility of a bone spur as a cause of your heel pain. A bone spur, if it is present in this location, is probably not the cause of your pain, but it is evidence that your plantar fascia has been exerting excessive force on your heel bone. X-ray images can also help determine if you have arthritis or whether other, more rare problems, stress fractures, bone tumors-are contributing to your heel pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
Careful attention to footwear is critical. Every effort should be made to wear comfortable shoes with proper arch support, fostering proper foot posture. Should arch supports prove insufficient, an orthotic shoe should be considered. Fortunately, most cases of plantar fasciitis respond well to non-operative treatment. Recovery times however vary enormously from one athlete to another, depending on age, overall health and physical condition as well as severity of injury. A broad period between 6 weeks and 6 months is usually sufficient for proper healing. Additionally, the mode of treatment must be flexible depending on the details of a particular athlete’s injury. Methods that prove successful in one patient, may not improve the injury in another. Early treatment typically includes the use of anti-inflammatory medication, icing, stretching activities, and heel inserts and splints. Cortisone injections may be necessary to achieve satisfactory healing and retard inflammation. In later stages of the rehabilitation process, typically after the first week, ice should be discontinued and replaced with heat and massage.

Surgical Treatment
In cases that do not respond to any conservative treatment, surgical release of the plantar fascia may be considered. Plantar fasciotomy may be performed using open, endoscopic or radiofrequency lesioning techniques. Overall, the success rate of surgical release is 70 to 90 percent in patients with plantar fasciitis. Potential risk factors include flattening of the longitudinal arch and heel hypoesthesia as well as the potential complications associated with rupture of the plantar fascia and complications related to anesthesia.
What Is Plantar Fasciitis
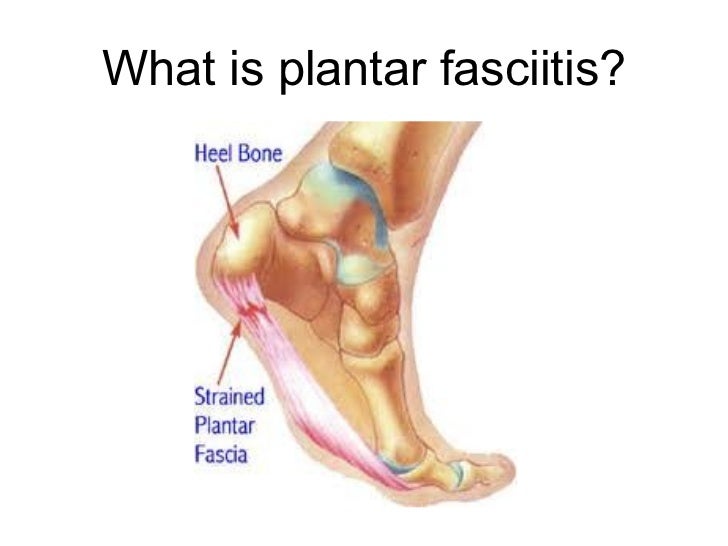
Overview
The plantar fascia is a tough and flexible band of tissue that runs under the sole of the foot. It connects the heel bone with the bones of the foot, and acts as a kind of shock absorber to the foot. Sudden damage, or damage that occurs over many months or years, can cause tiny tears (microtears) to develop inside the tissue of the plantar fascia. This can cause the plantar fascia to thicken, resulting in heel pain. The surrounding tissue and the heel bone can also sometimes become inflamed.
Causes
Each time we take a step forward, all of our body weight first rests on the heel of one foot. As our weight moves forward, the entire foot begins to bear the body's weight, and the foot flattens and this places a great deal of pressure and strain on the plantar fascia. There is very little elasticity to the plantar fascia, so as it stretches only slightly; it pulls on its attachment to the heel. If the foot is properly aligned this pull causes no problems. However, if the foot is "pronated" (the foot rolls outward at the ankle, causing a break down of the inner side of the shoe), the arch falls excessively, and this causes an abnormal stretching of the relatively inflexible plantar fascia, which in turn pulls abnormally hard on the heel. The same pathology occurs with "supination" (the rolling inward of the foot, causing a break down of the outer side of the shoe). Supinated feet are relatively in flexible; usually have a high arch, and a short or tight plantar fascia. Thus as weight is transferred from the heel to the remainder of the foot, the tight plantar fascia hardly stretches at all, and pulls with great force on its attachment to the heel.
Symptoms
When plantar fasciitis occurs, the pain is typically sharp and usually unilateral (70% of cases).Heel pain worsens by bearing weight on the heel after long periods of rest. Individuals with plantar fasciitis often report their symptoms are most intense during their first steps after getting out of bed or after prolonged periods of sitting. Improvement of symptoms is usually seen with continued walking. Numbness, tingling, swelling, or radiating pain are rare but reported symptoms. If the plantar fascia continues to be overused in the setting of plantar fasciitis, the plantar fascia can rupture. Typical signs and symptoms of plantar fascia rupture include a clicking or snapping sound, significant local swelling, and acute pain in the sole of the foot.
Diagnosis
X-rays are a commonly used diagnostic imaging technique to rule out the possibility of a bone spur as a cause of your heel pain. A bone spur, if it is present in this location, is probably not the cause of your pain, but it is evidence that your plantar fascia has been exerting excessive force on your heel bone. X-ray images can also help determine if you have arthritis or whether other, more rare problems, stress fractures, bone tumors-are contributing to your heel pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
Plantar fasciitis is usually controlled with conservative treatment. Following control of the pain and inflammation an orthotic (a custom made shoe insert) will be used to stabilize your foot and prevent a recurrence. Over 98% of the time heel spurs and plantar fasciitis can be controlled by this treatment and surgery can be avoided. The orthotic prevents excess pronation and prevents lengthening of the plantar fascia and continued tearing of the fascia. Usually a slight heel lift and a firm shank in the shoe will also help to reduce the severity of this problem. The office visit will be used for careful examination and review to distinguish plantar fasciitis and plantar heel pain syndrome from other problems, many of which are outlined below. It is important to distinguish between a stress reaction of the calcaneus and plantar fasciitis. A feature of many calcaneal stress fractures is pain on lateral and medial compression of the calcaneus.
Surgical Treatment
The majority of patients, about 90%, will respond to appropriate non-operative treatment measures over a period of 3-6 months. Surgery is a treatment option for patients with persistent symptoms, but is NOT recommended unless a patient has failed a minimum of 6-9 months of appropriate non-operative treatment. There are a number of reasons why surgery is not immediately entertained including. Non-operative treatment when performed appropriately has a high rate of success. Recovery from any foot surgery often takes longer than patients expect. Complications following this type of surgery can and DO occur! The surgery often does not fully address the underlying reason why the condition occurred therefore the surgery may not be completely effective. Prior to surgical intervention, it is important that the treating physician ensure that the correct diagnosis has been made. This seems self-evident, but there are other potential causes of heel pain. Surgical intervention may include extracorporeal shock wave therapy or endoscopic or open partial plantar fasciectomy.
Work Outs For Charcot Foot
Pain across the bottom of the foot at any point between the heel and the ball of the foot is often referred to as "arch pain” Although this description is non-specific, most arch pain is due to strain or inflammation Bunions Callous of the plantar fascia (a long ligament on the bottom of the foot). Wearing inappropriate footwear or foot problems like athlete's foot and Morton's neuroma are some of the factors that cause burning feet sensation.
If changing your shoes isn't helping to solve your foot pain, it is time for us to step in. Contact Dr. Jeff Bowman at Houston Foot Specialists for treatment that will keep your feet feeling great. Inserting arch support insoles in the shoes is also a good option.
If you see just a thin line connecting the ball of your foot to your heel, you have high arches. If you have flat feet or high arches, you're more likely to get plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the tissue along the bottom of your foot. Without proper arch support, you can have pain in your heels, arch, and leg. You can also develop bunions and hammertoes, which can become painful,” says Marlene Reid, a podiatrist, or foot and ankle doctor, in Naperville, IL. Shoes with good arch support and a slightly raised heel can help ward off trouble. Laces, buckles, or straps are best for high arches. See a foot doctor to get fitted with custom inserts for your shoes. Good running shoes, for example, can prevent heel pain, stress fractures , and other foot problems that can be brought on by running. A 2-inch heel is less damaging than a 4-inch heel. If you have flat feet, opt for chunky heels instead of skinny ones, Reid says.
Another solution is to wear custom foot orthotics, like ezWalker ® Performance Custom Orthotics, in your shoes to help correct your body posture, stabilize your balance, relieve pain during follow-through and evenly redistribute your weight on your feet. EzWalker® Custom Orthotics are specifically made for each of your feet to properly support your arches while reducing pressure on the balls of your feet. With ezWalker® Custom Orthotics, you'll walk from lateral heel to medial forefoot for better biomechanics of your entire body. This condition manifests as a skin lesion that assumes a ring-like pattern. It can affect any region of the body, right from the scalp to the foot. One such common home remedy is the use of bleach. Many people claim that this is a very effective ringworm treatment.
Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa: A condition that causes blistering of the skin because of a mutation of a gene which in normal conditions helps in the formation of thread-like fibers that are anchoring filaments, which fix the epidermis to the basement membrane. Kanner Syndrome: Also referred to as Autism, this is one of the neuropsychiatric conditions typified by deficiencies in communication and social interaction, and abnormally repetitive behavior. Kaposi's Sarcoma: A kind of malignancy of the skin that usually afflicts the elderly, or those who have problems in their immune system, like AIDS. For example, a year of perfect health is regarded as equivalent to 1.0 QALY.
If changing your shoes isn't helping to solve your foot pain, it is time for us to step in. Contact Dr. Jeff Bowman at Houston Foot Specialists for treatment that will keep your feet feeling great. Inserting arch support insoles in the shoes is also a good option.
If you see just a thin line connecting the ball of your foot to your heel, you have high arches. If you have flat feet or high arches, you're more likely to get plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the tissue along the bottom of your foot. Without proper arch support, you can have pain in your heels, arch, and leg. You can also develop bunions and hammertoes, which can become painful,” says Marlene Reid, a podiatrist, or foot and ankle doctor, in Naperville, IL. Shoes with good arch support and a slightly raised heel can help ward off trouble. Laces, buckles, or straps are best for high arches. See a foot doctor to get fitted with custom inserts for your shoes. Good running shoes, for example, can prevent heel pain, stress fractures , and other foot problems that can be brought on by running. A 2-inch heel is less damaging than a 4-inch heel. If you have flat feet, opt for chunky heels instead of skinny ones, Reid says.

Another solution is to wear custom foot orthotics, like ezWalker ® Performance Custom Orthotics, in your shoes to help correct your body posture, stabilize your balance, relieve pain during follow-through and evenly redistribute your weight on your feet. EzWalker® Custom Orthotics are specifically made for each of your feet to properly support your arches while reducing pressure on the balls of your feet. With ezWalker® Custom Orthotics, you'll walk from lateral heel to medial forefoot for better biomechanics of your entire body. This condition manifests as a skin lesion that assumes a ring-like pattern. It can affect any region of the body, right from the scalp to the foot. One such common home remedy is the use of bleach. Many people claim that this is a very effective ringworm treatment.

Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa: A condition that causes blistering of the skin because of a mutation of a gene which in normal conditions helps in the formation of thread-like fibers that are anchoring filaments, which fix the epidermis to the basement membrane. Kanner Syndrome: Also referred to as Autism, this is one of the neuropsychiatric conditions typified by deficiencies in communication and social interaction, and abnormally repetitive behavior. Kaposi's Sarcoma: A kind of malignancy of the skin that usually afflicts the elderly, or those who have problems in their immune system, like AIDS. For example, a year of perfect health is regarded as equivalent to 1.0 QALY.
Concerning Achilles Tendonitis
Overview
 The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects the calf muscles to the heel and is active during almost all activities including walking, jumping, and swimming. This dense tendon can withstand large forces, but can become inflamed and painful during periods of overuse. Pain results from inflammation (tendonitis) or a degenerating tendon (tendinosis). Achilles tendon pathologies include rupture and tendonitis. Many experts now believe, however, that tendonitis is a misleading term that should no longer be used, because signs of true inflammation are almost never present on histologic examination. Instead, the following histopathologically determined nomenclature has evolved. Paratenonitis: Characterized by paratenon inflammation and thickening, as well as fibrin adhesions. Tendinosis: Characterized by intrasubstance disarray and degeneration of the tendon.
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects the calf muscles to the heel and is active during almost all activities including walking, jumping, and swimming. This dense tendon can withstand large forces, but can become inflamed and painful during periods of overuse. Pain results from inflammation (tendonitis) or a degenerating tendon (tendinosis). Achilles tendon pathologies include rupture and tendonitis. Many experts now believe, however, that tendonitis is a misleading term that should no longer be used, because signs of true inflammation are almost never present on histologic examination. Instead, the following histopathologically determined nomenclature has evolved. Paratenonitis: Characterized by paratenon inflammation and thickening, as well as fibrin adhesions. Tendinosis: Characterized by intrasubstance disarray and degeneration of the tendon.
Causes
Achilles tendonitis most commonly occurs due to repetitive or prolonged activities placing strain on the Achilles tendon. This typically occurs due to excessive walking, running or jumping activities. Occasionally, it may occur suddenly due to a high force going through the Achilles tendon beyond what it can withstand. This may be due to a sudden acceleration or forceful jump. The condition may also occur following a calf or Achilles tear, following a poorly rehabilitated sprained ankle or in patients with poor foot biomechanics or inappropriate footwear. In athletes, this condition is commonly seen in running sports such as marathon, triathlon, football and athletics.
Symptoms
Symptoms include pain in the heel and along the tendon when walking or running. The area may feel painful and stiff in the morning. The tendon may be painful to touch or move. The area may be swollen and warm. You may have trouble standing up on one toe.
Diagnosis
During an examination of the foot and ankle, you doctor will look for the following signs, Achilles tendon swelling or thickening. Bone spurs appearing at the lower part of the tendon at the back of the hell. Pain at the middle or lower area of the Achilles tendon. Limited range of motion of the foot and ankle, and a decreased ability to flex the foot. Your doctor may perform imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendinitis. X-rays show images of the bones and can help the physician to determine if the Achilles tendon has become hardened, which indicated insertional Achilles tendinitis. MRI scans may not be necessary, but they are important guides if you are recommended to have surgical treatment. An MRI can show the severity of the damage and determine what kind of procedure would be best to address the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Relieving the stress is the first course of action. Treatment involves ice therapy and activity modification to reduce inflamation. Active stretching and strengthening exercises will assist rehabilitation of the gastrocnemius-soleus complex. When placed in a heeled shoe, the patient will immediately notice a difference, compared to flat ground. It is recommended that the patient be fitted with proper shoes & orthotics to control pronation and maintain proper alignment, relieving the stress on the achilles tendon. Tightness in the tendon itself can be helped by an extra heel lift added to the orthotics. The patient can expect a slow recovery over a period of months.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery should be considered to relieve Achilles tendinitis only if the pain does not improve after 6 months of nonsurgical treatment. The specific type of surgery depends on the location of the tendinitis and the amount of damage to the tendon. Gastrocnemius recession. This is a surgical lengthening of the calf (gastrocnemius) muscles. Because tight calf muscles place increased stress on the Achilles tendon, this procedure is useful for patients who still have difficulty flexing their feet, despite consistent stretching. In gastrocnemius recession, one of the two muscles that make up the calf is lengthened to increase the motion of the ankle. The procedure can be performed with a traditional, open incision or with a smaller incision and an endoscope-an instrument that contains a small camera. Your doctor will discuss the procedure that best meets your needs. Complication rates for gastrocnemius recession are low, but can include nerve damage. Gastrocnemius recession can be performed with or without d?bridement, which is removal of damaged tissue. D?bridement and repair (tendon has less than 50% damage). The goal of this operation is to remove the damaged part of the Achilles tendon. Once the unhealthy portion of the tendon has been removed, the remaining tendon is repaired with sutures, or stitches to complete the repair. In insertional tendinitis, the bone spur is also removed. Repair of the tendon in these instances may require the use of metal or plastic anchors to help hold the Achilles tendon to the heel bone, where it attaches. After d?bridement and repair, most patients are allowed to walk in a removable boot or cast within 2 weeks, although this period depends upon the amount of damage to the tendon. D?bridement with tendon transfer (tendon has greater than 50% damage). In cases where more than 50% of the Achilles tendon is not healthy and requires removal, the remaining portion of the tendon is not strong enough to function alone. To prevent the remaining tendon from rupturing with activity, an Achilles tendon transfer is performed. The tendon that helps the big toe point down is moved to the heel bone to add strength to the damaged tendon. Although this sounds severe, the big toe will still be able to move, and most patients will not notice a change in the way they walk or run. Depending on the extent of damage to the tendon, some patients may not be able to return to competitive sports or running. Recovery. Most patients have good results from surgery. The main factor in surgical recovery is the amount of damage to the tendon. The greater the amount of tendon involved, the longer the recovery period, and the less likely a patient will be able to return to sports activity. Physical therapy is an important part of recovery. Many patients require 12 months of rehabilitation before they are pain-free.
Prevention
As with all injuries, prevention is your best defense especially with injuries that are as painful and inconvenient as Achilles tendonitis. Options for how to prevent Achilles tendonitis include, stretching- Stretching properly, starting slowly, and increasing gradually will be critical if you want to avoid Achilles tendonitis. To help maintain flexibility in the ankle joint, begin each day with a series of stretches and be certain to stretch prior to, and after, any exercise or excessive physical activity. Orthotics and Heel Support- Bio-mechanically engineered inserts and heel cups can be placed in your shoes to correct misalignments or bolster the support of your foot and are available without a prescription. The temporary heel padding that these provide reduces the length that the Achilles tendon stretches each time you step, making it more comfortable to go about your daily routine. Proper Footwear- Low-heeled shoes with good arch support and shock absorption are best for the health of your foot. Look into heel wedges and other shoe inserts to make sure that your everyday foot mechanics are operating under ideal conditions.
 The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects the calf muscles to the heel and is active during almost all activities including walking, jumping, and swimming. This dense tendon can withstand large forces, but can become inflamed and painful during periods of overuse. Pain results from inflammation (tendonitis) or a degenerating tendon (tendinosis). Achilles tendon pathologies include rupture and tendonitis. Many experts now believe, however, that tendonitis is a misleading term that should no longer be used, because signs of true inflammation are almost never present on histologic examination. Instead, the following histopathologically determined nomenclature has evolved. Paratenonitis: Characterized by paratenon inflammation and thickening, as well as fibrin adhesions. Tendinosis: Characterized by intrasubstance disarray and degeneration of the tendon.
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It connects the calf muscles to the heel and is active during almost all activities including walking, jumping, and swimming. This dense tendon can withstand large forces, but can become inflamed and painful during periods of overuse. Pain results from inflammation (tendonitis) or a degenerating tendon (tendinosis). Achilles tendon pathologies include rupture and tendonitis. Many experts now believe, however, that tendonitis is a misleading term that should no longer be used, because signs of true inflammation are almost never present on histologic examination. Instead, the following histopathologically determined nomenclature has evolved. Paratenonitis: Characterized by paratenon inflammation and thickening, as well as fibrin adhesions. Tendinosis: Characterized by intrasubstance disarray and degeneration of the tendon.
Causes
Achilles tendonitis most commonly occurs due to repetitive or prolonged activities placing strain on the Achilles tendon. This typically occurs due to excessive walking, running or jumping activities. Occasionally, it may occur suddenly due to a high force going through the Achilles tendon beyond what it can withstand. This may be due to a sudden acceleration or forceful jump. The condition may also occur following a calf or Achilles tear, following a poorly rehabilitated sprained ankle or in patients with poor foot biomechanics or inappropriate footwear. In athletes, this condition is commonly seen in running sports such as marathon, triathlon, football and athletics.
Symptoms
Symptoms include pain in the heel and along the tendon when walking or running. The area may feel painful and stiff in the morning. The tendon may be painful to touch or move. The area may be swollen and warm. You may have trouble standing up on one toe.
Diagnosis
During an examination of the foot and ankle, you doctor will look for the following signs, Achilles tendon swelling or thickening. Bone spurs appearing at the lower part of the tendon at the back of the hell. Pain at the middle or lower area of the Achilles tendon. Limited range of motion of the foot and ankle, and a decreased ability to flex the foot. Your doctor may perform imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendinitis. X-rays show images of the bones and can help the physician to determine if the Achilles tendon has become hardened, which indicated insertional Achilles tendinitis. MRI scans may not be necessary, but they are important guides if you are recommended to have surgical treatment. An MRI can show the severity of the damage and determine what kind of procedure would be best to address the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Relieving the stress is the first course of action. Treatment involves ice therapy and activity modification to reduce inflamation. Active stretching and strengthening exercises will assist rehabilitation of the gastrocnemius-soleus complex. When placed in a heeled shoe, the patient will immediately notice a difference, compared to flat ground. It is recommended that the patient be fitted with proper shoes & orthotics to control pronation and maintain proper alignment, relieving the stress on the achilles tendon. Tightness in the tendon itself can be helped by an extra heel lift added to the orthotics. The patient can expect a slow recovery over a period of months.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery should be considered to relieve Achilles tendinitis only if the pain does not improve after 6 months of nonsurgical treatment. The specific type of surgery depends on the location of the tendinitis and the amount of damage to the tendon. Gastrocnemius recession. This is a surgical lengthening of the calf (gastrocnemius) muscles. Because tight calf muscles place increased stress on the Achilles tendon, this procedure is useful for patients who still have difficulty flexing their feet, despite consistent stretching. In gastrocnemius recession, one of the two muscles that make up the calf is lengthened to increase the motion of the ankle. The procedure can be performed with a traditional, open incision or with a smaller incision and an endoscope-an instrument that contains a small camera. Your doctor will discuss the procedure that best meets your needs. Complication rates for gastrocnemius recession are low, but can include nerve damage. Gastrocnemius recession can be performed with or without d?bridement, which is removal of damaged tissue. D?bridement and repair (tendon has less than 50% damage). The goal of this operation is to remove the damaged part of the Achilles tendon. Once the unhealthy portion of the tendon has been removed, the remaining tendon is repaired with sutures, or stitches to complete the repair. In insertional tendinitis, the bone spur is also removed. Repair of the tendon in these instances may require the use of metal or plastic anchors to help hold the Achilles tendon to the heel bone, where it attaches. After d?bridement and repair, most patients are allowed to walk in a removable boot or cast within 2 weeks, although this period depends upon the amount of damage to the tendon. D?bridement with tendon transfer (tendon has greater than 50% damage). In cases where more than 50% of the Achilles tendon is not healthy and requires removal, the remaining portion of the tendon is not strong enough to function alone. To prevent the remaining tendon from rupturing with activity, an Achilles tendon transfer is performed. The tendon that helps the big toe point down is moved to the heel bone to add strength to the damaged tendon. Although this sounds severe, the big toe will still be able to move, and most patients will not notice a change in the way they walk or run. Depending on the extent of damage to the tendon, some patients may not be able to return to competitive sports or running. Recovery. Most patients have good results from surgery. The main factor in surgical recovery is the amount of damage to the tendon. The greater the amount of tendon involved, the longer the recovery period, and the less likely a patient will be able to return to sports activity. Physical therapy is an important part of recovery. Many patients require 12 months of rehabilitation before they are pain-free.
Prevention
As with all injuries, prevention is your best defense especially with injuries that are as painful and inconvenient as Achilles tendonitis. Options for how to prevent Achilles tendonitis include, stretching- Stretching properly, starting slowly, and increasing gradually will be critical if you want to avoid Achilles tendonitis. To help maintain flexibility in the ankle joint, begin each day with a series of stretches and be certain to stretch prior to, and after, any exercise or excessive physical activity. Orthotics and Heel Support- Bio-mechanically engineered inserts and heel cups can be placed in your shoes to correct misalignments or bolster the support of your foot and are available without a prescription. The temporary heel padding that these provide reduces the length that the Achilles tendon stretches each time you step, making it more comfortable to go about your daily routine. Proper Footwear- Low-heeled shoes with good arch support and shock absorption are best for the health of your foot. Look into heel wedges and other shoe inserts to make sure that your everyday foot mechanics are operating under ideal conditions.